
Understanding Chapter 13 Bankruptcy in Texas
A lot of Texans live most of their lives without ever seeing a snowball. Nevertheless, all Texans know what happens when you roll a snowball down a hill. It gets bigger and bigger until it wrecks everything in its path. The same is true of debt. It starts small, but if you ignore it, it can grow out of control. If you find yourself in this situation, filing chapter 13 bankruptcy in Texas may be a viable solution to help you regain control of your finances.

Debt snowballs are something most Texans are intimately familiar with. If Paul has trouble making car payments, he shifts money from other bills, like credit card payments, to the car note. Then, when he almost inevitably falls behind on car payments, the late fees add up quickly. The combined late fees create a snowball so big that it wrecks everything in its path.
At this point, Paul has basically two choices. He can brace for impact at the bottom of the hill (repossession), or he can file chapter 13 bankruptcy, put his missed car payments in his chapter 13 plan, and retake control over his financial situation. This page examines some nuts and bolts of chapter 13 bankruptcy in Texas and highlights ways this federal debt relief program makes life-altering financial changes.
What Is Chapter 13 Bankruptcy in Texas? — A Guide
Texas is composed of four federal districts to handle bankruptcy cases. The Northern, Southern, Eastern, and Western districts are available to serve you if you’re weighing options to catch up on bills, like Paul.
Chapter 13 is a 3 to 5 year payment plan that also offers Texans a discharge of general unsecured debts (like credit cards and medical bills) at the end of this plan. While in the plan, you are able to catch up on missed payments, like mortgage arrears and vehicle arrears. You are also able to pay back debts that are otherwise not dischargeable, like certain taxes and domestic support obligations. Chapter 13 also allows you to pay off secured debts, like vehicle loans, often at reduced interest and sometimes reduced principal.
Chapter 13 is also often used by Texans who don't qualify for chapter 7 bankruptcy, or those who have assets that are not exempt. Chapter 13 allows these filers to get relief and keep their assets.
Key Benefits of Filing Chapter 13 in Texas
Chapter 13 can be utilized in several different ways to help Texans regain control of their finances. Here are some of the key benefits:

Immediate Protection from Creditors
As soon as a chapter 13 case is filed, you are protected by the automatic stay. This is court-ordered protection from the U.S. Bankruptcy Court that halts most creditor actions.
Stopping Foreclosure
The automatic stay can immediately stop creditor actions toward your home, including foreclosure. Meanwhile, you can pay back any mortgage arrears through your chapter 13 plan and come out of the plan completely caught up, avoiding foreclosure.
Stopping Repossession
Chapter 13 can stop a potential vehicle repossession and let you repay past-due amounts over time while you keep making regular payments going forward.
Paying Off Secured Debts (Vehicle Loans)
In many cases Texans are able to pay off a vehicle in their chapter 13 plan—often at reduced interest and sometimes reduced principal via a "cram down".
Catching Up or Paying Off Priority Debts (Taxes and Domestic Support)
Keep Important Property:
If you have non-exempt assets, chapter 13 may let you keep them by paying their value over time through your plan.
Protection for Co-Signers on Consumer Debts:
The co-debtor stay (protection for co-signers) may shield qualifying co-obligors on consumer accounts while your plan is active.
Eligibility Criteria for Chapter 13 Bankruptcy in Texas
There are specific requirements to be able to file and stay in a chapter 13 plan.
Regular Income
To stay in chapter 13 in Texas, you must have steady income (wages, business revenue, retirement, etc.) sufficient to make plan payments over the 36- or 60-month plan.
Means Test & Texas Median Income
The length of your plan depends on your current monthly income compared to the Texas median. If your income is below the median, you may qualify for a 36-month plan. If it is above, you will likely need a 60-month plan.
Texas Median Income (Updated Annually)
Below are the current median income figures for Texas:
- 1 person: $63,448
- 2 people: $83,037
- 3 people: $95,391
- 4 people: $110,719
- 5 people: $121,819
- 6 people: $132,919
- 7 people: $144,019
- 8 people: $155,119
Debt Limits
For cases filed April 1, 2025 through March 31, 2028, limits are approximately $526,700 unsecured and $1,580,125 secured (noncontingent, liquidated). These amounts are adjusted over time. Those who are over these limits usually consider chapter 11 bankruptcy as an alternative.
Must Be Current on Filing Taxes
You must be current on filing your taxes. You cannot have any missing or pending returns that need to be filed.
Credit Counseling
You must complete a credit counseling course from an approved provider within 180 days before filing. You will receive a certificate to include with your petition.
The Chapter 13 Bankruptcy Process in Texas
The most challenging part of the chapter 13 process is making the plan payments over the 36- or 60-month period. The initial steps are similar to chapter 7, but there are some differences. Here’s a general step-by-step overview of the chapter 13 process in Texas:
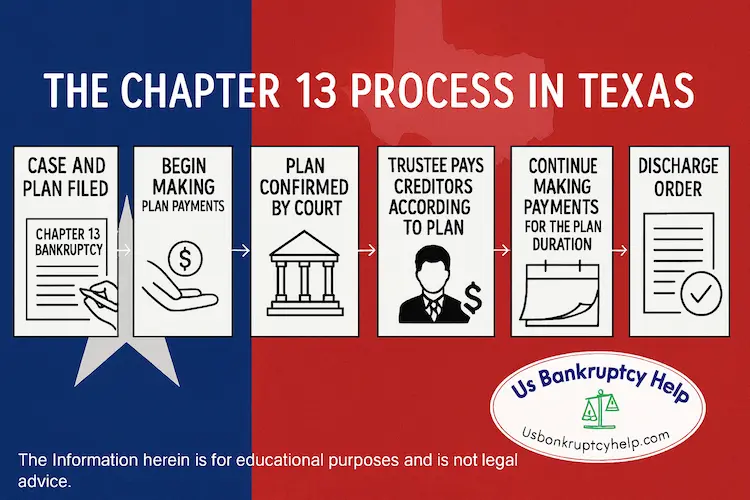
Credit Counseling
To qualify to file chapter 13 in Texas, you have to complete a credit counseling course from an approved provider within 180 days before filing. You’ll receive a certificate to include with your petition.
File Your Case
Your petition, schedules, and proposed plan are filed in your Texas district and division. Filings can be done at the clerk’s office in your division, or electronically. Filings disclose all of your assets, income, expenses, debts, and your plan strategy.
Automatic Stay
Filing triggers the automatic stay (bankruptcy protection), which generally halts most creditor actions like foreclosures, repossessions, and wage garnishments.
Plan Review & Confirmation
The trustee and creditors review your plan. A § 341 meeting (meeting of creditors) is held, usually within 20–40 days of filing. The trustee may request additional documents. After any objections are resolved, the trustee usually stipulates to confirmation, and the court confirms the plan. A confirmation hearing can be held, but this is usually not necessary.
Make Plan Payments
You begin payments (usually within 30 days of filing). The trustee distributes funds to creditors according to the confirmed plan. Payments can often be auto-debited; some trustees allow checks or online portals.
Financial Management Course
To qualify for a discharge in chapter 13, filers must take a financial management course that is similar to the credit counseling course.
Discharge
After you complete plan terms and required courses, remaining dischargeable debts are wiped out and the case closes.
Texas Bankruptcy Courts & Filing Locations
Texas has four federal bankruptcy districts to administer chapter 13 cases. Your division—based on residence or principal place of business—controls where you file and attend hearings. Use the placeholders below for addresses and clerk details:
- Northern District of Texas — Divisions include Dallas, Fort Worth, Lubbock, Amarillo, Abilene, San Angelo, Wichita Falls. Dallas Division Clerk’s Office: Earle Cabell Federal Building, 1100 Commerce St., Room 1254, Dallas, TX 75242-1496 • Hours: Mon–Fri, 8:30 a.m.–4:30 p.m.
- Southern District of Texas — Divisions include Houston, Galveston, Victoria, Corpus Christi, Laredo, McAllen, Brownsville. Houston Division (Bob Casey U.S. Courthouse): 515 Rusk Ave., Houston, TX 77002 • Hours: Mon–Fri, 8:00 a.m.–5:00 p.m.
- Eastern District of Texas — Divisions include Plano/Sherman, Tyler, Beaumont, Lufkin, Texarkana. Plano Division Clerk’s Office: U.S. Bankruptcy Court, 660 North Central Expy., Suite 300B, Plano, TX 75074 • Hours: Mon–Fri, 8:00 a.m.–4:00 p.m.
- Western District of Texas — Divisions include San Antonio, Austin, El Paso, Waco, Midland, Pecos, Del Rio. San Antonio Division Clerk’s Office: Hipolito F. Garcia Federal Bldg. & U.S. Courthouse, 615 E. Houston St., Room 597, San Antonio, TX 78205 • Hours: Mon–Fri, 8:00 a.m.–12:00 p.m. and 1:00 p.m.–4:00 p.m. (closed 12–1 for lunch)
§ 341 meetings (meeting of creditors) in Texas are frequently held by phone or video; your official notice provides the date, time, and connection instructions.
Seeking Professional Help
Bankruptcy in Texas is governed by federal law, local rules, and division-specific practices. A Texas chapter 13 attorney will help you navigate these state and federal waters, tailor your plan, protect exempt property, and manage trustee requirements.
Chapter 13 is a complicated process that should only be undertaken with the help of an attorney. It requires careful budgeting, accurate income and expense analysis, and a well-constructed plan. An experienced Texas bankruptcy attorney can help you evaluate your options, build a feasible plan, and guide you through the process to maximize your chances of success.
Additionally, chapter 13 often requires responses and defenses to motions, objections, and other court filings. An attorney can help you respond appropriately and protect your interests. Attorneys often have to object to creditors' proofs of claim, and negotiation is required to resolve disputes. A Texas bankruptcy attorney is highly advised to help chapter 13 debtors have a successful case.
Post-Confirmation Issues
Often after the chapter 13 plan is confirmed, Texans face issues that could jeopardize their plan. Job change, job loss, car accidents, medical emergencies, and other life events can impact your ability to make plan payments. Such issues require immediate attention to keep your plan intact.
Modifying Your Chapter 13 Plan
The good news is that chapter 13 is flexible. If your income changes, a modified plan can be filed to reflect the change. Amended plans need to be confirmed, so the confirmation process is repeated. If you are having trouble making plan payments, contact your attorney and trustee immediately to discuss options.
Converting to Chapter 7
If you simply cannot make plan payments, or you have a major unexpected expense, you may be able to convert your chapter 13 case to chapter 7. This should be carefully considered, as it requires a close look at your budget and assets.
Life After Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
Rebuild Credit
Most Texans find that by the time they are done with their chapter 13 plan, their credit is already on the way to recovery. You can further rebuild by making on-time payments, keeping credit card balances low, and avoiding new debt.
Maintain Strong Financial Habits
After the 3 to 5 year payment plan, chapter 13 teaches many Texans how to budget their income. Keep a realistic budget, build an emergency buffer, avoid unnecessary expenses, and save for future goals.
Chapter 13 Offers Many Practical Options
Choosing chapter 13 Texas can provide a structured, court-approved path to cure arrears, reorganize debt, and protect what matters. When paired with up-to-date Texas exemptions and accurate income analysis, a well-built plan can move you toward stability with fewer surprises.
Educate yourself, follow the steps, and lean on local guidance to complete your plan and receive a discharge. If you believe you are facing a major financial event, like garnishment, repossession, or foreclosure, act quickly. The sooner you file, the sooner you can stop creditor actions and start rebuilding your financial life.
Who Are the Chapter 13 Bankruptcy Trustees in Texas, and What Do They Do?
In every chapter 13 case, a court-appointed chapter 13 trustee evaluates your plan, conducts the § 341 meeting, collects monthly payments, and sends funds to creditors after confirmation. The trustee is independent from both you and the judge.
What Chapter 13 Trustees Do
- Review your petition, schedules, pay proofs, tax returns, and proposed plan for accuracy and feasibility.
- Conduct the meeting of creditors and request any additional documents needed to verify your case.
- Receive monthly plan payments and distribute according to the confirmed plan and the Code.
- Monitor ongoing compliance (tax filings, income changes, insurance, domestic support obligations, etc.).
- File recommendations or objections and report case status to the Court as needed.
Texas Chapter 13 Trustees & Contact Information
Texas has multiple standing chapter 13 trustees. Your assignment depends on the district and division where you file. Always follow your Notice of Bankruptcy Case for the official trustee name and payment instructions.
- Southern District — Houston Division
Tiffany D. Castro, Chapter 13 Trustee
Office: 1220 Augusta Dr., Suite 500, Houston, TX 77057 • Phone: (713) 722-1200
Website: ch13hou.com
Payments: PO Box 740, Memphis, TN 38101-0740; ePay/TFS options listed on trustee site (verify on your notice).
David G. Peake, Chapter 13 Trustee
Office: 9660 Hillcroft, Suite 430, Houston, TX 77096 • Phone: (713) 283-5400
Website: 13Network – Peake
Payments: PO Box 2158, Memphis, TN 38101-2158; ePay available (verify on your notice).
Also in the Southern District (Corpus Christi / Brownsville / McAllen)
Yvonne V. Valdez, Chapter 13 Trustee
Office: 555 N. Carancahua St., Suite 600, Corpus Christi, TX 78401 • Phone: (361) 883-5786
Website: ch13cctx.com
Payments: PO Box 703, Memphis, TN 38101-0703 (verify on your notice). - Northern District — Dallas & Fort Worth Divisions
Dallas — Thomas D. (Tom) Powers, Chapter 13 Trustee
Office: 5601 Executive Dr., Suite 300, Irving, TX 75038 • Phone: (214) 855-9200
Website: dallasch13.com
Payments: Standing Chapter 13 Trustee, PO Box 1958, Memphis, TN 38101-1958 (verify on your notice).
Fort Worth — Tim Truman, Chapter 13 Trustee
Office: 6851 N.E. Loop 820, Suite 300, North Richland Hills, TX 76180 • Phone: (817) 770-8500
Website: 13Network – Truman
Payments: PO Box 2285, Memphis, TN 38101-2285 (verify on your notice).
Fort Worth — Pam Bassel, Chapter 13 Trustee
Office: 7001 Blvd 26, Suite 150, North Richland Hills, TX 76180 • Phone: (817) 916-4710
Website: 13Network – Bassel
Payments: PO Box 1201, Memphis, TN 38101-1201 (verify on your notice).
Other Northern Divisions (Abilene / Amarillo / Lubbock / San Angelo / Wichita Falls)
Katherine L. Davis, Chapter 13 Trustee
Office: 1407 Buddy Holly Ave., Lubbock, TX 79401 • Phone: (806) 748-1980
Website: ch13-12westtex.org • 13Network – Davis
Payments: PO Box 94210, Lubbock, TX 79493-4210 (verify on your notice). - Western District — San Antonio & Austin Divisions
San Antonio — Mary K. Viegelahn, Chapter 13 Trustee
Office: 10500 Heritage Blvd., Suite 201, San Antonio, TX 78216 • Phone: (210) 824-1460
Website: sach13.com
Payments: PO Box 85510, Chicago, IL 60689-5510 (effective June 1, 2025); older notices may list PO Box 1231, San Antonio, TX 78294-1231—follow your notice.
Austin/Waco — G. Ray Hendren, Jr., Chapter 13 Trustee
Office: 4505 Spicewood Springs Rd., Suite 205, Austin, TX 78759 • Phone: (512) 474-6309
Website: 13Network – Hendren
Payments: PO Box 85511, Chicago, IL 60689-5511 (verify on your notice).
Austin — Deborah B. Langehennig, Chapter 13 Trustee
Office: 6201 Guadalupe St., Austin, TX 78752 • Phone: (512) 912-0305
Website: ch13austin.com
Payments: PO Box 298, Memphis, TN 38101-0298; TFS/ePay options on trustee site (verify on your notice).
El Paso — Stuart C. Cox, Chapter 13 Trustee
Office: 1760 N. Lee Trevino Dr., El Paso, TX 79936 • Phone: (915) 598-6769
Website: ch13elpaso.com
Payments: See trustee site for TFS Bill Pay and mailing details (verify on your notice). - Eastern District — Plano/Sherman, Tyler, Beaumont
Plano/Sherman — Carey D. Ebert, Chapter 13 Trustee
Correspondence: PO Box 941166, Plano, TX 75094-1166 • Phone: (972) 943-2580
Website: planoch13.com
Payments: Carey D. Ebert, Chapter 13 Trustee, PO Box 628, Tyler, TX 75710 (verify on your notice).
Tyler/Beaumont — Lloyd T. Kraus, Chapter 13 Trustee
Office: 110 N. College Ave., Suite 1200, Tyler, TX 75702 • Phone: (903) 593-7777
Website: ch13tyler.com
Payments: P.O. Box 734, Tyler, TX 75710; TFS/MoneyGram available (verify on your notice).
Note: Trustee names, lockbox addresses, payment portals, and remote-appearance procedures are subject to change. Rely on the most recent court notices and the trustee’s website for official instructions.
Why This Matters to You
Knowing how your trustee and division operate helps you stay compliant, avoid delays, and complete your plan on time. On-time payments, organized records, and quick responses to requests are the fastest route to a successful discharge.
More Resources
For a broader overview, visit our national chapter 13 guide, and if you’re comparing options, start with chapter 7 vs. chapter 13.
Texas Chapter 13 Success Stories
Houston Family Saves Their Home and Ends Wage Garnishments
A married couple in Houston fell three months behind on their mortgage after medical bills and reduced overtime. Credit card lawsuits followed, and a wage garnishment was about to start. By filing chapter 13 bankruptcy in Texas, they stopped the garnishment immediately and used the plan to catch up $9,800 in mortgage arrears over 60 months while keeping current going forward. Unsecured creditors received a small pro-rata distribution based on the family’s disposable income. Because the plan also addressed past-due HOA fees and a lingering toll-road violation, the couple finished with their home intact, no active collections, and a clean path to rebuild.
- • Kept the house and cured arrears over time
- • Stopped wage garnishment and collection calls
- • Consolidated debts into one affordable monthly payment
Dallas Rideshare Driver Keeps Car and Restructures Tax Debt
A single parent in Dallas relied on a late-model sedan for rideshare income but was two payments behind and facing repossession. They also owed recent IRS debt that could not be wiped out in chapter 7. A chapter 13 Texas plan re-aged the auto loan, spread the arrears over 36 months, and paid the priority IRS balance in full without additional penalties. With budget-friendly plan payments and court protection, the driver kept the vehicle, stabilized cash flow, and finished the case with current taxes and a paid-off car—critical wins for long-term financial stability.
- • Stopped repossession and kept essential transportation
- • Paid priority IRS taxes in full inside the plan
- • Reduced interest and consolidated into one payment
San Antonio Small Business Owner Protects Tools and Streamlines Debt
A San Antonio handyman juggled business credit cards, equipment financing, and a medical collection. High interest and seasonal income swings made it impossible to keep up. Filing chapter 13 bankruptcy in Texas allowed him to protect tools and equipment needed for work, pay down a small secured balance on a compressor at a fair value, and send a modest dividend to unsecured creditors. The plan also caught up a past-due utility that threatened service. With predictable payments over 48 months, he kept operating the business, retained his clients, and exited the plan without losing crucial gear.
- • Preserved tools of the trade and business income
- • Managed secured and unsecured debts under court supervision
- • Avoided disruptive shutoffs and collection lawsuits
Results vary and depend on your specific facts, income, and Texas exemptions. This is general information, not legal advice. Always consult your Notice of Bankruptcy Case and your attorney for trustee-specific payment instructions.
Frequently Asked Questions About Chapter 13 Bankruptcy in Texas
Where Are Texas Chapter 13 Hearings Held, and Can I Appear by Phone or Video?
Hearing calendars are set by the U.S. Bankruptcy Courts for the Northern, Southern, Eastern, and Western Districts of Texas, with divisions such as Dallas, Fort Worth, Houston, San Antonio, Austin, El Paso, Plano/Sherman, Tyler, and Beaumont. Remote appearances may be allowed depending on the judge and the type of hearing. Your Notice of Hearing controls; never record or stream a court proceeding.
Where Are § 341 “Meeting of Creditors” Held for Texas Chapter 13 Cases, and How Do I Attend?
The U.S. Trustee Program schedules § 341 meetings; many Texas meetings are conducted by phone or video with a dial-in option. Your official notice lists the date, time, and connection details. Have a government photo ID and proof of Social Security number ready, and join a few minutes early.
What Are the Current Chapter 13 Debt Limits in Texas?
Eligibility limits are federal and apply statewide. For cases filed April 1, 2025 through March 31, 2028, the general thresholds are about $526,700 unsecured and $1,580,125 secured (noncontingent, liquidated). Check for updates if you file later.
How Long Does a Chapter 13 Plan Last in Texas, and How Are Payments Set?
Most Texas chapter 13 plans last 3 to 5 years. Plan length and monthly payments depend on income, allowable expenses, and required repayment of secured arrears and priority debts. Debtors below the Texas median income typically propose 36 months; above-median debtors usually propose 60 months unless all allowed unsecured claims will be paid sooner. Current median figures: [insert Texas median income numbers by household size].
Will Chapter 13 Stop Foreclosure or Repossession in Texas?
Yes. Filing creates an automatic stay that generally stops foreclosures, repossessions, and most collection actions immediately. In chapter 13, you can spread past-due mortgage or car payments over the plan term (subject to court approval). Creditors can request relief from the stay, so make payments on time and follow your plan.
Explore Bankruptcy Help by State
Browse our state guides to learn exemptions, means test rules, costs, and local procedures. Use these links to jump between states and compare your options.
- Arizona
- California
- Colorado
- Florida
- Georgia
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Maryland
- Michigan
- New York
- Ohio
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Virginia
- Wisconsin